Foot fungus is a common condition affecting the skin and nails of the feet. This condition is typically not harmful, but it can bring unwanted change to the skin on the affected foot. Understanding what causes this condition, the symptoms it produces, and the available treatment methods helps individuals recognize potential infections and know how to address them.
What Is Foot Fungus?
Foot fungus is a fungal infection often caused by dermatophytes, microorganisms that thrive in warm, damp environments. These fungi are commonly found on the skin without causing problems, but when the environment allows them to multiply, infection can result. The most frequent places for exposure include communal showers, locker rooms, and swimming pool decks. Walking barefoot increases contact with fungi. Wearing tightly enclosed footwear that traps moisture also promotes the growth of fungi.
Individuals who experience persistent dampness due to heavy sweating are at greater risk. Sharing personal items such as towels, socks, or shoes with another person who has foot fungus can contribute to the spread of the infection. Certain health conditions associated with a weakened immune system, such as diabetes, as well as the use of some medications, may also contribute to an increased susceptibility.
What Are the Symptoms?
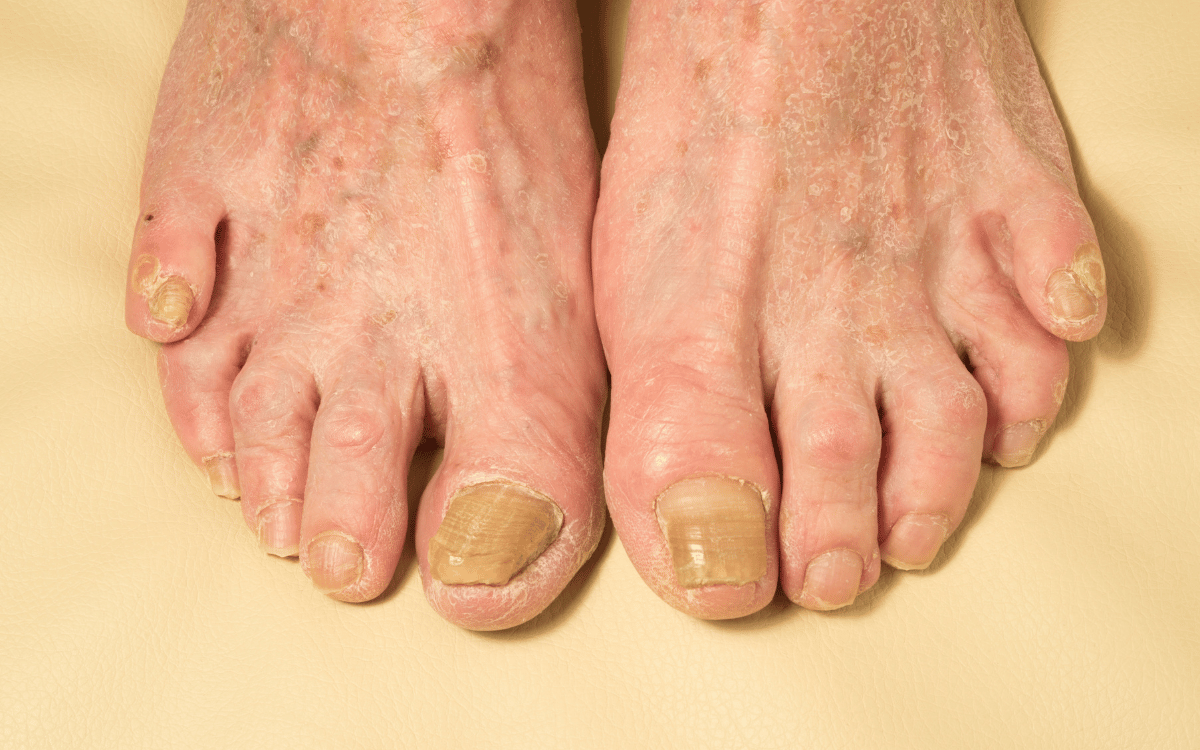
Foot fungus most often affects the skin between the toes, but can also involve the soles, tops, and sides of the feet as well as the toenails. Common symptoms include itching in the affected area that are accompanied by burning or stinging sensations. The skin may appear cracked, begin peeling, or develop scaling that often extends to the sides of the feet. Fluid-filled blisters form in some cases. The skin may become discolored, showing shades of red, purple, or gray, and a noticeable odor can develop.
When foot fungus spreads to the toenails, the nails may show discoloration. The affected nails may become thickened, brittle, and sometimes crumble or detach from the nail bed. These changes in the nails can develop gradually.
How Is It Treated?
The general approach to managing foot fungus involves hygiene measures, limiting moisture, using available antifungal preparations, and reducing opportunities for reinfection. Diligent foot hygiene is beneficial. Washing the feet daily with soap and water, followed by thorough drying, may help limit fungal overgrowth. Wearing clean, dry socks helps manage perspiration. Regularly changing socks and allowing footwear time to dry between uses may further restrict the fungus’s preferred environment.
More persistent or widespread infections may be treated with prescription medications provided by a healthcare provider. These treatments may take the form of stronger topical antifungal agents for the skin or oral antifungal medications. Prescribed oral medications can be selected when topical options have not resolved the infection. Limiting the spread or recurrence of foot fungus includes avoiding the sharing of socks, shoes, or towels with others and using sandals or shower shoes in communal wet areas. These preventive practices can reduce contact with fungal spores.
Seek Professional Foot Care
Professional evaluation becomes warranted if symptoms do not respond to standard measures, persist, or worsen. Individuals with underlying health conditions should seek medical guidance promptly if symptoms arise. Healthcare providers and foot specialists can differentiate fungal infections from other skin problems. They can recommend a suitable plan that may include topical or oral antifungal treatments, as well as other supportive interventions.